Experiment: Nipple water troughs for dairy calves

Background
Cross-sucking is a common abnormal behaviour in group-housed dairy calves, linked to welfare concerns and management practices. This study evaluates whether nipple-equipped water troughs can reduce this behaviour, promoting more natural drinking patterns and improved welfare outcomes.
Goals
- Assess the effect of nipple water troughs on the frequency and duration of cross-sucking in group-housed calves
- Evaluate behavioural changes in response to different water provision systems
- Determine whether nipple water troughs support more natural oral behaviours in calves after milk feeding
Results
- 42% reduction in cross-sucking in calves with nipple access vs. open troughs (p = 0.003)
- No negative impact on growth (weaning weights: p = 0.788)
- Longer water trough visits and nighttime water intake in groups of calves with nipple water troughs
Cross-sucking Behavior
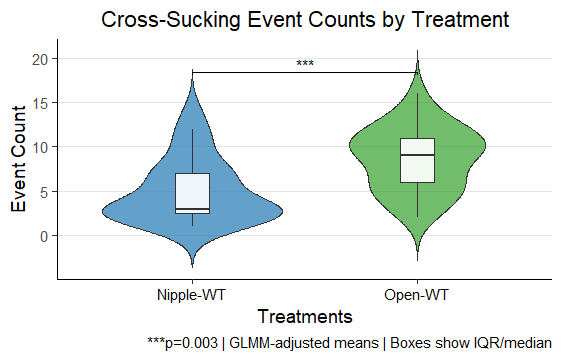
Calves with nipple water troughs exhibited less cross-sucking events than calves with open water troughs during pre-weaning period.
Water intake
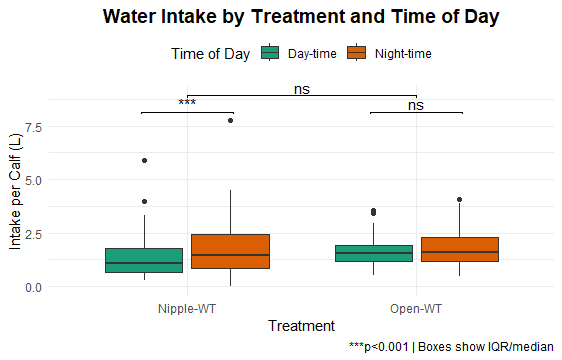
Calves with nipple water troughs consumed more water during night-time.
Weight Gain
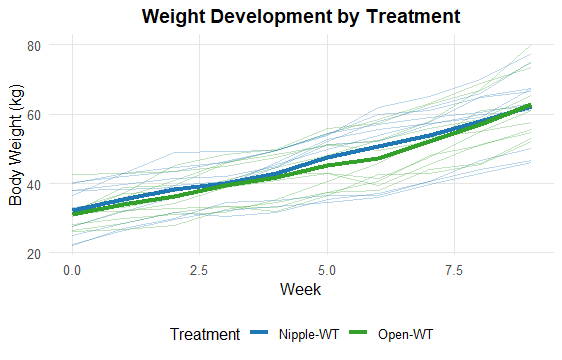
There was no difference in the performance of calves with nipple or open water troughs.
Skills Used:
R
Excel
Data collection
Data visualization
Applied Ethology
Animal Science